Cost optimization is again a priority for tech companies. Some engineers are uneasy about AI replacing them with codeless test automation (TA). But are these platforms as powerful as their marketing? What ROI can businesses expect in a real-world setting? What exactly do you need to maximize the return?
At MindK, we’ve been stress-testing AI capabilities at all levels, from requirements analysis to rapid MVP development. Test automation is a natural path forward. Implementing codeless TA on several large projects revealed significant advantages in accessibility, test creation speed, and cost savings.
However, our hands-on experience also highlights the limitations and hidden complexities of codeless solutions. Features like test recording, automatic locator generation, and AI-powered auto-healing didn’t always work as seamlessly as advertised.
In this article, we’ll examine how well the most popular codeless test automation (TA) features match the marketing hype. We’ll also reveal a detailed measurement of the codeless TA Net Profit and Total Investment Cost.
Table of contents:
- The sweet promise of codeless test automation
- How does it stack up to the bitter reality?
- Top codeless features and our experience using them
- Test recording
- Automatic UI Element
- AI Auto-healing
- Our verdict on these features
- How to maximize codeless test automation ROI
- Evaluate tools deliberately
- Define the scope: codeful vs codeless
- Measure the ROI beyond surface-level time savings
The sweet promise of codeless test automation
Codeless TA allows you to create, execute, and maintain automated tests without writing code. Instead of scripting, engineers use visual interfaces, drag-and-drop components, and predefined test actions. This provides a number of benefits:
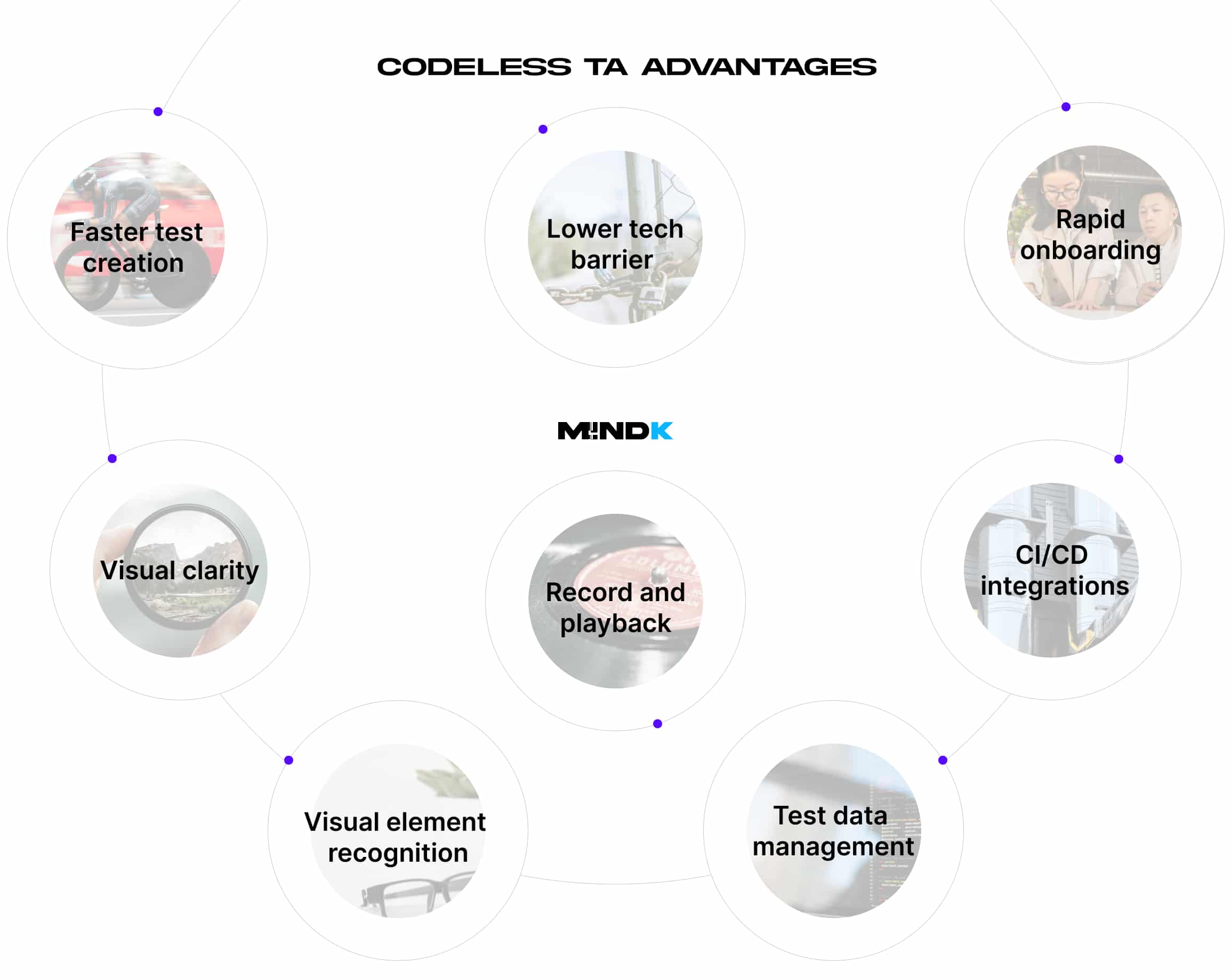
- Faster test creation. With a highly intuitive interface, design tests in hours instead of days. This is especially valuable when automating basic functional flows or smoke tests.
- Lower technical barrier. Business analysts, product owners, and other non-techies can actively contribute to TA, reducing dependency on automation engineers.
- Rapid onboarding. New team members are up to speed quickly, making it easier to scale QA efforts as the project grows.
- Visual clarity. Tests built with codeless tools are often more readable and intuitive for business stakeholders.
- Built-in features like record-and-playback, visual element recognition, test data management, and CI/CD integrations reduce the need for complex configs.
Like any technology, codeless test automation has limitations. To objectively assess its pros and cons, our team integrated the technology into a complex healthcare project and measured every performance metric. Here’s what we’ve seen.
How does it stack up to the bitter reality?
In our hands-on experience, codeless test automation is particularly valuable for quickly automating high-priority, straightforward test cases and enabling non-technical contributors to participate in the testing process.
Complex scenarios, API-heavy workflows, or performance-sensitive areas, however, often found us reaching back to coded automation for greater control and reliability. Although codeless TA is marketed as “simple,” it requires a solid understanding of underlying testing concepts, including locators, waiters, test data, and assertions.
Codeless TA is a powerful accelerator, but its success depends on how and where it’s used. It works best as a complementary solution, not a replacement for all testing needs.
Now, let’s take a closer look at the most marketed codeless TA features and their usefulness in a real-world project.
Top codeless features and our experience using them
Codeless test automation tools promote a set of powerful features designed to make tests faster, easier, and more resilient. These include test recording, automatic UI element creation, and AI-powered auto-healing capabilities.
While these features are heavily marketed and look promising on paper, our practical experience revealed significant limitations.
Test recording
Most codeless tools allow users to interact with the application while the platform captures actions like clicks, form inputs, and navigations.
Sounds convenient. However, we found that recording tests in reality often introduces unnecessary complexity and hidden fragility. For example:
- Recording generated numerous redundant steps. These ranged from previously defined selected elements to including unnecessary actions like double-clicks and hover events.
- We were frequently required to manually add extra steps to ensure test reliability. This included clearing fields before filling them, waiting for specific elements to load, or reusing existing actions to reduce duplication.
- In many cases, we realized that it was more efficient and more reliable to create tests from scratch using existing elements and reusable components, rather than relying on the recorder’s output.
The promise of “record once and go” rarely held up in practice.
Automatic UI element creation
Codeless platforms also offer automatic element detection and locator generation during test recording. This should make tests more resilient to UI changes. However, we encountered serious limitations:
- Auto-generated locators were frequently overcomplicated. They relied on long, fragile XPath expressions, dynamic IDs, or easily changeable text content.
- Locators were often tied to specific text or page states at the moment of recording, leading to frequent test failures when the app evolved.
- Element names generated by the tool were usually unintuitive and inconsistent. Test steps were hard to read and maintain, so we had to spend extra time renaming each element manually for a consistent naming style.
This added an unexpected layer of maintenance overhead that undermined the advertised benefits of the feature.
AI-powered auto-healing
This is perhaps the most hyped feature in modern codeless platforms. AI auto-healing engines are claimed to detect any changes to elements and automatically update the locator to prevent test failures.
This should make tests more resilient to UI changes. However, we encountered some serious limitations:
- The AI engine often matched the wrong elements. For instance, mistaking a button in a modal for one on the main page, leading to false positives. The test passed, but the intended functionality was not actually verified.
- This undermined the reliability of test results and introduced the risk of silent failures, where the test appeared green but actually validated the wrong behavior.
- Ultimately, we found that relying on auto-healing without careful validation could lead to a false sense of confidence in the test suite.
Our verdict on these features
While features like test recording, automatic element creation, and AI auto-healing save time in some cases, they rarely work as seamlessly as advertised.
IIn numerous situations, more time was spent cleaning up and maintaining tests than would’ve been by creating them manually with a clear, structured approach. Our experience underscores an important point: codeless tools are not a magic solution. They require careful oversight, a solid understanding of testing principles, and a willingness to balance speed with accuracy.
Our team achieved the best results by using codeless features selectively in combination with good test design practices and a well-defined scope.
So, how can you make the most out of codeless test automation?
How to maximize codeless test automation ROI
When we embarked on the journey to implement test automation for our project, we faced a common challenge: balancing the need for speed and accessibility with the system’s complexity.
The product had both standard user flows and highly complex scenarios with multiple third-party integrations, dynamic UI components, and API-heavy backends.
From the outset, we knew that a one-size-fits-all approach wouldn’t work. So, we set out to define a hybrid strategy that would leverage both traditional TA and codeless test automation, assigning the right tool to the right job.
Evaluate codeless test automation tools deliberately
There are more than 50 test automation tools to choose from. It’s easy to get overwhelmed or make a marketing-driven choice.
Some of the tools are prohibitively expensive in the long run. We disqualified such tools as they negate any potential cost savings. The team ran a thorough investigation, trialed the best codeless platforms, and compared them across key criteria:
- Functionality. We evaluated whether each tool could handle both UI and API testing, support data-driven tests, manage dynamic locators, and provide reliable cross-browser capabilities.
- Ease of use. How quickly can testers create and maintain test cases without deep technical knowledge?
- Flexibility. How well does each platform adapt to unique workflows, including support for custom logic, dynamic content, and integration-heavy scenarios?
- Pricing model. We analyzed licensing structures and scalability, ensuring the long-term cost would remain sustainable as our test suite grew.
- Integration capabilities. How smoothly does each tool integrate with our CI/CD pipeline, version control systems, and existing reporting tools?
- Maintenance: How easy is it to update tests in the context of frequent UI changes, API adjustments, and evolving business requirements? Key factors are the ability to efficiently modify element locators, manage shared test components, and propagate updates across multiple test cases without excessive manual effort.
- Debugging and troubleshooting: What support does the tool provide for analyzing test failures, including step-by-step logs, visual playback, and error messages? We found that while codeless platforms provided helpful visual tools, diagnosing complex issues, such as async timing problems, API failures, or third-party integration bugs, was often less transparent than in code-based frameworks.
This evaluation phase is crucial. It revealed each tool’s strengths and limitations, not just in initial test creation but also in the long-term sustainability of our automation efforts. It helped our team narrow down the choice to a handful of trusted platforms, including BrowserStack, Postman, Apache JMeter, and TestRail. Each tool is a solid choice depending on the project specifics. However, we won’t advertise one particular tool above the others for the sake of objectivity.
Define the scope for codeful vs. codeless TA
Based on our evaluation, we defined a clear division of responsibilities:
- Traditional coded automation should be used for complex scenarios where we require maximum control. The examples include API-heavy workflows and tests involving multiple systems and integrations. This gave us the flexibility to handle advanced logic, custom assertions, and non-standard test flows that codeless platforms often struggled with.
- Codeless test automation would focus on standard, high-priority business flows, such as core UI journeys and straightforward API tests. This allowed us to speed up test creation and involve non-technical team members in building and maintaining the tests.
By playing to the strengths of each approach, you can accelerate automation without sacrificing quality or flexibility.
Measure ROI beyond surface-level time savings
From the very beginning of the automation initiative, we committed to precisely tracking the effort required for both new test development and ongoing test maintenance.
For the first couple of months, we closely monitored the time spent on each activity. The team documented the real effort needed for codeless automation vs. traditional coded tools. Our findings confirmed the earlier expectations:
- With codeless tools, the time required for creating new tests was up to 80% faster than developing equivalent tests in code.
- The time needed for test maintenance (updating locators, handling changes in UI or API endpoints, and debugging failures) was also reduced, although the gap narrowed in more complex scenarios.
However, we wanted to go beyond surface-level time savings. We took a holistic approach, factoring in not only the time and effort for test creation and maintenance but also all parameters contributing to Net Profit and Total Investment Cost:
- Licensing fees and subscription costs.
- Time savings that translate into increased productivity.
- Reduced risk of regression defects leading to faster releases.
- The potential cost of debugging complex failures and vendor lock-in risks.
Our key takeaway? While codeless TA showed clear efficiency benefits, particularly for straightforward test cases and scenarios, the overall ROI depended heavily on the mix of test types, the complexity of the workflows, and the long-term maintenance effort.
Codeless was a strong accelerator for simple, repetitive flows. However, the ROI advantage diminished for complex scenarios, reinforcing the need for a hybrid approach. For more details, check our in-depth article with ROI calculations.
Conclusion
Codeless TA delivers on many promises, especially when it comes to accelerating the initial creation of tests for standard, well-defined business flows. It allows us to involve non-technical team members in test design and helps in scaling test coverage faster than traditional automation.
We found that just like with AI agent development, teams still need strong practical experience in test automation to truly leverage codeless automation effectively. This includes an understanding of testing principles, best practices, and where codeless TA can and cannot be applied.
Without this expertise, there’s a real risk of fragile, unreliable test suites, wasted time, and unexpected costs. In other words, codeless doesn’t eliminate the need for skilled testers. It simply shifts the nature of the work.
That said, we believe it is a step in the right direction. Tools will become more accessible, AI capabilities will continue to improve, and the gap between technical and non-technical contributors will gradually narrow.
As with any innovation, the key is to experiment, learn, and adapt. So, don’t hesitate to contact us if you have any questions or need help with codeless test automation on your project.