More than 4 years have passed since the EU adopted the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR). Now everyone in the business of apps has to comply with the privacy regulations or face fines up to €20 million. So, here’s our guide to GDPR compliance for software developers and entrepreneurs.
Are you liable to GDPR?
Check out the following criteria to our find if your solution is subject to privacy regulations:
- Do EU citizens use your solution?
- Is there a subscription function on your website?
- Do you have any comments sections?
- Can users log in to your website with third-party apps?
If you answered yes at least to one question, congratulations, you are a definite candidate to the GDPR. So better start reading on how to implement GDPR compliance.
Further reading: everything you need to know about GDPR software requirements and how to prepare your company for the new age of privacy.
How to be GDPR compliant?
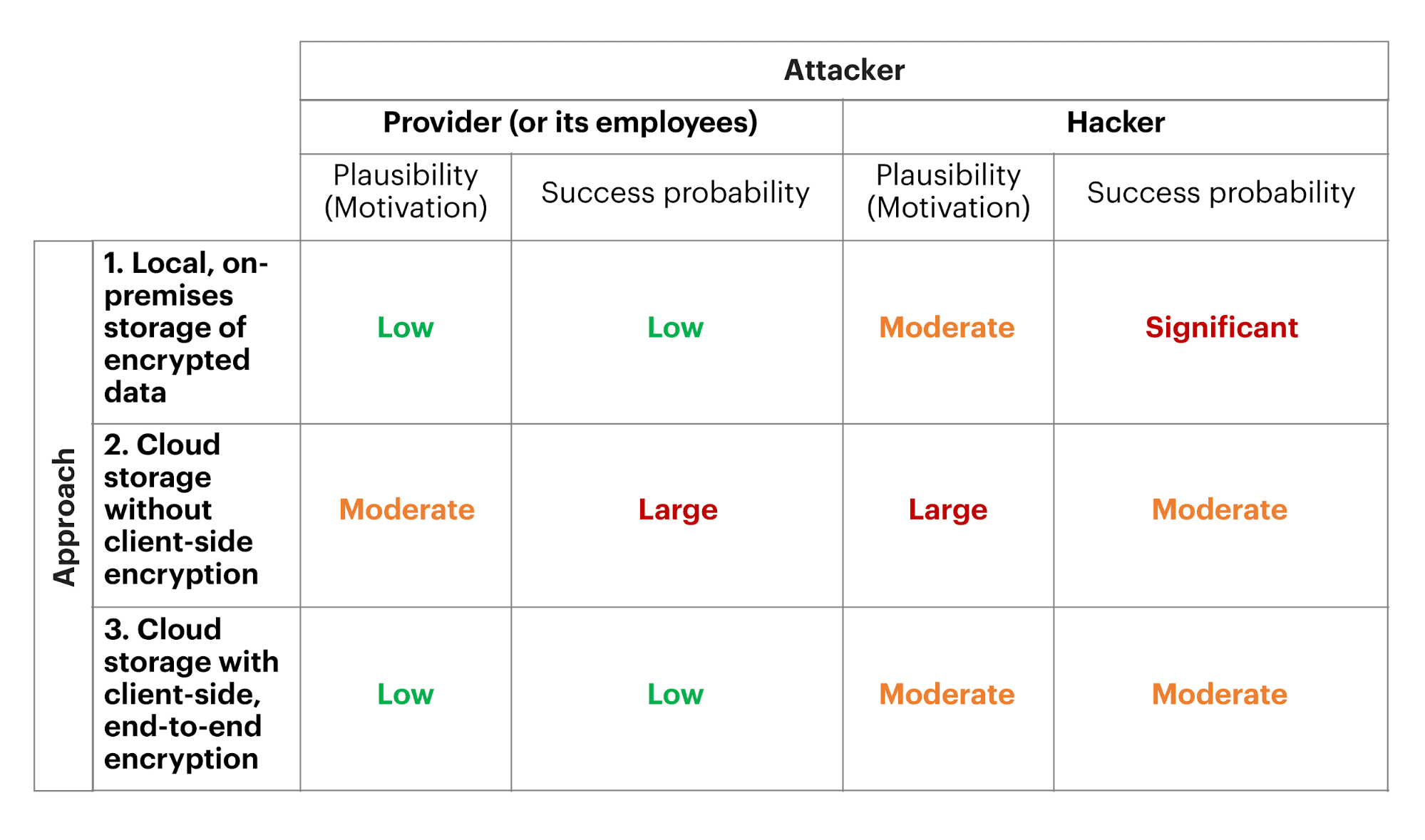
1. Consider whether you really need all the data you collect
The first step to GDPR compliant software is to check what kind of personal data it stores.
Do you really need it?
The best course for the privacy-conscious future is to collect only the bare minimum of personal data.
2. Encrypt all personal data
Encryption scrambles data in a way that makes it unintelligible for those who don’t have the decryption keys. Although it’s often mentioned as a key factor of GDPR compliance, the word “encryption”is only mentioned 4 times throughout the GDPR text:
- “…implement measures to mitigate those risks, such as encryption.” (P51. (83))
- “…appropriate safeguards, which may include encryption” (P121 (4.e))
- “…including inter alia as appropriate: (a) the pseudonymisation and encryption of personal data.” (P160 (1a))
- “…unintelligible to any person who is not authorised to access it, such as encryption” (P163 (3a))
As any cybersecurity expert would tell you, data breaches are inevitable.
In July 2015, hackers attacked Ashley Madison and stole more than 25 GB of personal data from the adultery dating website.
The information, including names, emails, and addresses, was stored as plain text which allowed anyone to track the would-be cheaters. This negligence resulted in a wave of blackmail, ruined careers, and broken marriages.
Website owners had to pay over $11 million to settle ensuing lawsuits.
Moreover, at least three people have committed suicide due to Ashley Madison breach.
Source: tresorit.com
But what if for some legitimate reason, such as cost-efficiency or drop in performance, you can’t use encryption as a part of your data protection policy?
In such a case, you should either gather enough evidence to back up your claims or use alternative methods such as pseudonymization.
3. Consider HTTPs as an essential part of your application
Contact us” forms often contain personal data such as emails, phones, or home addresses. If you store and send this information as plain text, you’re opening the door to hackers.
So again, use encryption for the “contact us” forms. Also, inform your clients how you store this data and for how long.
The next step is to employ HTTPS, a secure version of the HTTP communication protocol.
It encrypts all the data sent between a client and a server using the SSL/TLS cryptographic protocols. When a user requests an HTTPS connection to your application, it sends him/her your SSL certificate that contains the key required to initiate the secure connection.
That’s why it’s important to receive an SSL certificate from a credible Certificate Authority and correctly install it.
Also, make sure that your certificate isn’t susceptible to the protocol vulnerabilities.
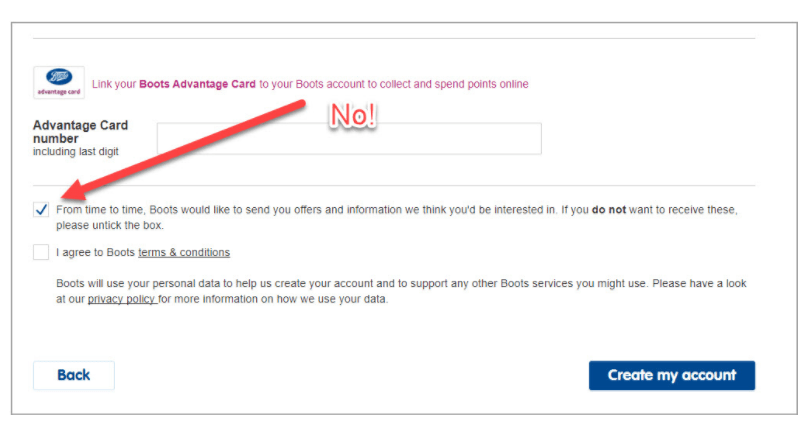
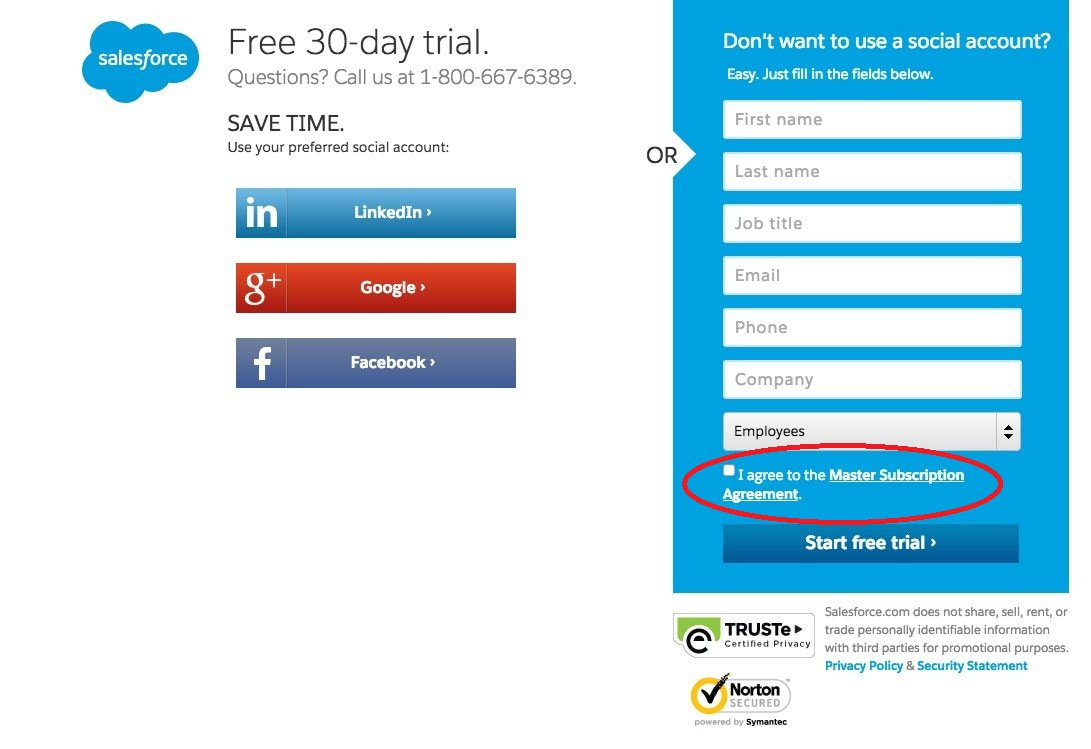
4. Get your consent forms in order
Forget about any kind of pre-ticked boxes.
Your consent forms must default to a “no” or be blank. In such a way you don’t force your users to actively opt-out.
Your consent forms must default to a “no” or be blank. In such a way you don’t force your users to actively opt-out.
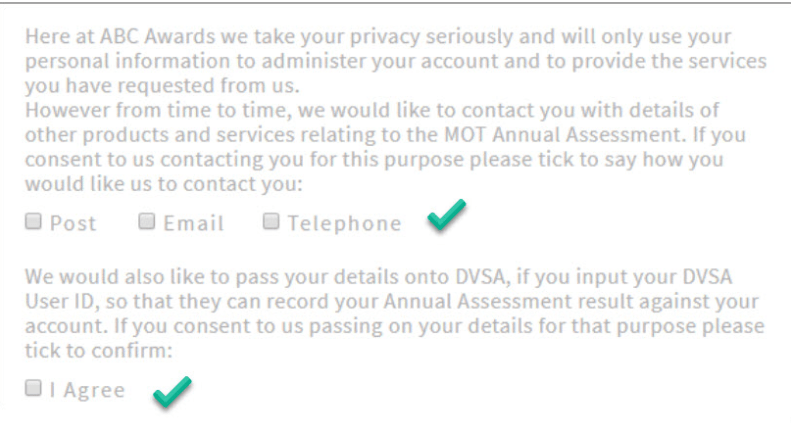
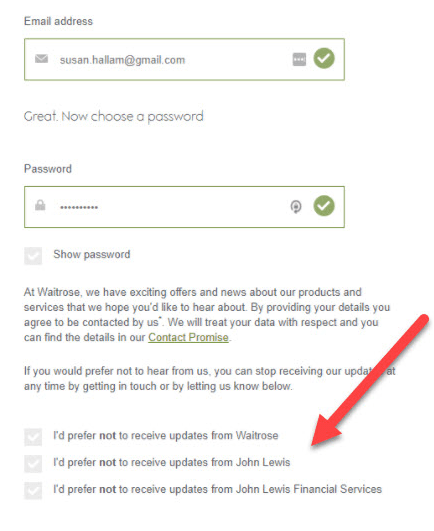
5. Implement granular opt-in
As a website owner, you want to occasionally reach out to your clients for marketing purposes. You need to ask explicit consent for each type of data processing you handle.
This means that if you’d like to sent promo materials via email, phone, and post, your consent form should have three separate opt-in boxes:
If all you need for your marketing is the email address, a marketing consent will suffice.
But if you use personalization, segmentation or targeting, you’ll need both the marketing consent and consent (or legitimate interest) to collect and profile any additional behavioral or demographic data.
6. Be specific about the third parties
If you pass your customers’ personal data to the third parties, you should accurately identify and name each of these parties in your consent forms.
Note how each permission in the picture above has its own checkbox. However, you’d have to opt-out of the permission instead of opt-in which is a big NO under GDPR.
Still, giving third parties access to the personal data of your users for analytics or other purposes is definitely a bad idea.
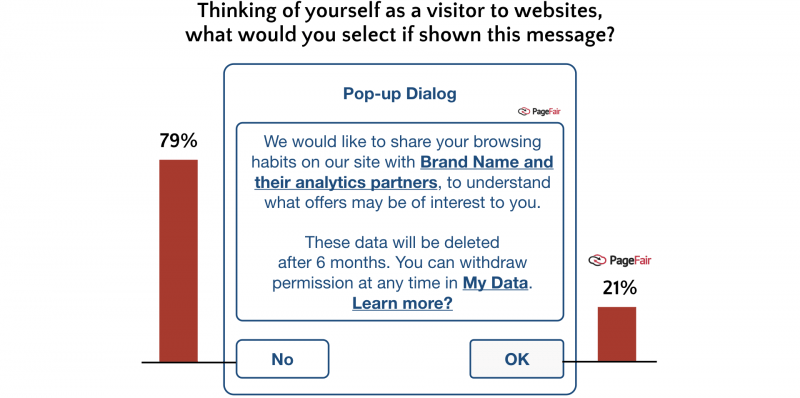
Source: PageFair.com
According to more than 300 industry experts, the majority of users don’t want third parties anywhere near their personal data.
The best decision might be using a self-hosted web analytics platform which guarantees that you will be the only one to collect, process and store personal data.
Note: GDPR doesn’t impact the usage of Google Analytics as it can’t track individual users.
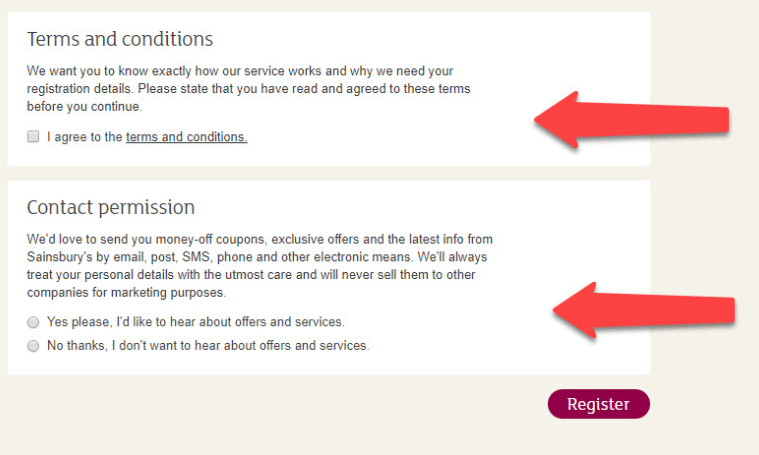
7. Separate the Terms and Conditions agreement from other consent forms
You’ll have to request Terms and Conditions agreement separately for any kind of personal data handling.
8. Make Terms and Conditions section highly visible
Under GDPR you’re no longer allowed to hide your Terms and Conditions or bury it in the fine print. The following scheme is no longer appropriate according to the regulation:
Users will have to acknowledge they’ve read the Terms and Conditions and agree to them before getting access to your app..
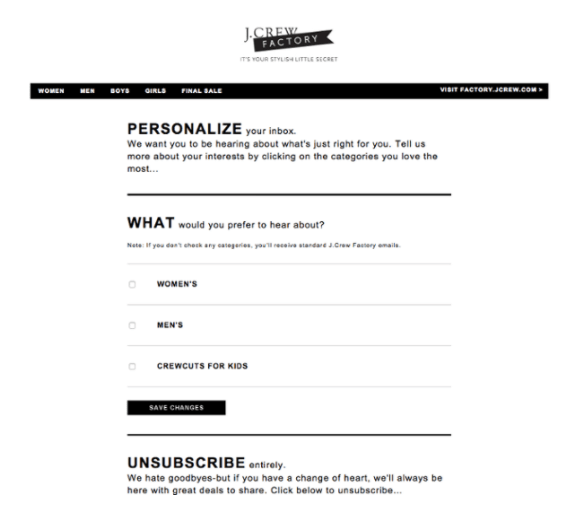
9. Make sure users can easily withdraw their consent
Due to the new GDPR principle – Right to be Forgotten – a user must be able to unsubscribe and remove his/her consent at any time. If, for example, you send newsletters to your customers, your links and emails should contain the “unsubscribe” feature.
But don’t despair if some users decided to unsubscribe from your mailout! With a dash of creativity, you can change their hearts and encourage them to resubscribe. Here’s an example which proves that even “unsubscribe” link can be at your best service:
10. Change your cookie policies
In the official GDPR document cookies are mentioned in the following context (Recital 30):
Natural persons may be associated with online identifiers […] such as internet protocol addresses, cookie identifiers or other identifiers […]. This may leave traces which, in particular when combined with unique identifiers and other information received by the servers, may be used to create profiles of the natural persons and identify them.
In 2020, you should either avoid using such cookies or find lawful ground for collecting and processing personal data:
- Legal obligations;
- Legitimate interests (as long as they don’t violate individual rights);
- Requirements for a contract execution (i.e. gathering payment data from contractors)
- User consent.
Under GDPR, the act of visiting your website for the first time doesn’t automatically grant consent for processing personal data. Even if you display “If you use this website, you accept cookies”, the consent case is not considered as “freely given” (Recital 42).
Granular consent still applies, so if you want to track your visitor behavior and use their data for advertising, you should obtain consent for each activity.
You’ll also have to allow visitors to easily withdraw their consent.
Remember, you can’t block access to your website for the users who withheld consent. And after they log out, you’ll have to destroy their cookies and sessions.
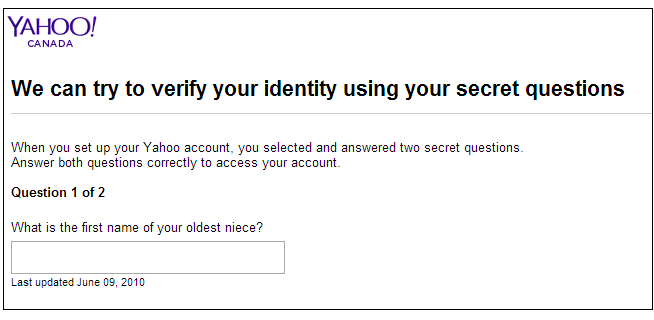
11. Avoid security questions that disclose personal information
When signing up for a web application, you will often get security questions:
This is a big NO for GDPR software compliance.
Since May 2018, security questions mustn’t contain any information related to the customer’s family, preferences, homes, etc.
The best option is to use two-factor authentication (2 FA), which combines a password with a phone number/fingerprints etc. Such systems are a powerful deterrent for cybercriminals.
If, for some reason, this option isn’t possible, let users create their own secret questions. Just warn them against disclosing personal information.
12. Inform users about logs containing their IP addresses
Check if your system uses IP addresses or location data in the authentication process. If your logs contain such data, you should inform users about the way you store them and how long they persist in your system.
Also, encrypt your logs and never store the particularly sensitive data (i.e passwords) in them.
13. Remove all personal data after being passed to payment gateways
This is a crucial step for e-commerce applications.If you use payment gateways, you are likely gathering customers personal data. In most cases, this data remains in your system.
This is illegal under the data protection regulation.
Your application must delete any personal data of your customers within a set period of time (e.g. 60 days).
Read more: how to choose the best payment gateway?
14. Allow users to reject your business intelligence tracking
E-commerce websites often track the visitors’ behavior and tastes to improve their recommendations. Under GDPR, such activities require a clear and explicit consent. You’ll also have to tell users how this data will be stored in your systems and for how long.
If a user rejects tracking, you’ll have to respect his or her choice.
15. Erase unsubscribed user data
E-commerce websites often track visitor behavior and tastes to improve recommendations.
Under the GDPR, such activities require a clear and explicit consent. You’ll also have to tell users how this data will be stored in your systems and for how long.
Wrapping up
Now you know how to become GDPR compliant.
In the privacy-conscious future, the ability to ensure security and transparency of your application will be a huge advantage. You can use this GDPR compliance checklist for software development to rise above competition and carve a niche in the changing markets.
And if the task seems too tough, you can always rely on MindK to take care of GDPR compliance for your software.
And of course, don’t forget to subscribe and download our ebook!